The power plant boiler is an important energy conversion device among the three major equipment in the power plant. Its function is to convert the chemical energy of the fuel into thermal energy, and use the thermal energy to heat the water in the boiler to make it superheated steam with sufficient quantity and certain quality (steam temperature, steam pressure) for use by the steam turbine.
The power plant boiler now has large capacity, high parameters, complex technology, high level of mechanization and automation, so the fuel is mainly coal, and the coal is made into pulverized coal before combustion, and then sent to the boiler to burn and release heat in the furnace. In general, the main working process of the boiler is the combustion of fuel, the transfer of heat, the heating and vaporization of water, and the superheating of steam.
The whole boiler consists of two parts: the boiler body and auxiliary equipment.
Boiler Body
The boiler body is indeed central to the operation of a power plant boiler, and it can be divided into two key components: the “pot” and the “furnace.”
1. The Pot:
- Definition: The “pot” refers to the pressure vessel where water is converted into steam.
- Function: Inside the pot, water is heated and transformed into steam. The design must handle the high pressure and temperature of the steam. The pot includes various components such as:
- Steam drum: Collects and separates steam from the water.
- Mud drum (if present): Collects impurities from the water.
- Tubes: Water-tube boilers have a series of tubes where water circulates, heated by the combustion gases from the furnace.
2. The Furnace:
- Definition: The “furnace” is the part of the boiler where fuel combustion takes place.
- Function: The furnace provides the heat necessary to turn water into steam. It includes the combustion chamber, where the fuel is burned, and the walls lined with water-filled tubes that absorb the generated heat.
- Components: The furnace also includes burners, grates (in solid fuel boilers), and refractory materials that protect the furnace structure from high temperatures.
Relationship Between Pot and Furnace:
- The furnace generates heat through the combustion of fuel, and this heat is transferred to the pot, where it converts water into steam. The design ensures efficient heat transfer and the safe containment of high-pressure steam.
Auxiliary Equipment
Auxiliary equipment includes ventilation equipment (forced and induced draft fans), fuel transportation equipment, pulverizing system, ash and dust removal equipment, desulfurization equipment, etc.
Types of Power Plant Boiler
Power plant Boiler is often categorized as either fire-tube boilers or water-tube boilers. This distinction is based on whether it is the generated heat or the water that passes through the tubes. There are many subtypes of boilers in each category used in different industries for various purposes.
Fire-Tube Boilers
Fire-tube boilers have tubes through which the hot gases, or “fire,” created from combustion pass through. The tubes are surrounded by a sealed tank of water, and as the heat passes through the tubes, it heats the water by the process of thermal conduction. Eventually, the water becomes hot enough to boil and converts into steam.
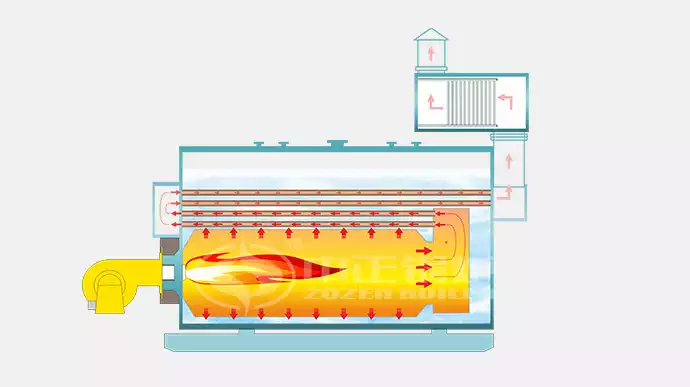
fire-tube boiler
Construction and Working Principle
- Components: Firebox, combustion chamber, tubes, and steam drum.
- Operation: Hot gases from combustion pass through the tubes, heating the surrounding water, which turns into steam.For more on boiler construction and repairs, visit Boiler Construction and Repairs.
Advantages and Applications
- Advantages: Simple construction, low cost, easy maintenance.
- Applications: Small to medium-scale industries, heating systems.
Water-Tube Boilers
Water-tube boilers use the opposite configuration compared to fire-tube boilers. With water-tube boilers, instead of the hot gases passing through tubes contained within the water, the water instead passes through tubes contained within the hot gases. This allows heat to be transferred by convection or thermal radiation, resulting in the water boiling into steam.
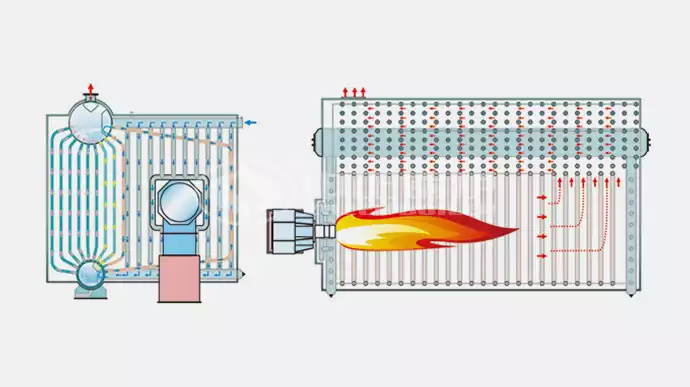
water tube boiler
Construction and Working Principle
- Components: Steam drum, water tubes, mud drum, and circulation pump.
- Operation: Water circulates through the tubes, heated by surrounding hot gases, converting it to steam.
Advantages and Applications
- Advantages: Higher efficiency, better heat transfer, and high steam pressure.
- Applications: Power plants, chemical processing industries, refineries.
Learn more about the need for different types of boilers by product or geography at Different Types of Boilers.
Working Process of Power Plant Boiler
1. Fuel Combustion
The boiler burns fuel (coal, natural gas, oil, or biomass) in a furnace to produce heat. In modern power plants, pulverized coal or natural gas is commonly used.
2. Heat Transfer
The heat from combustion is transferred to water contained in boiler tubes through the walls of the furnace. The water absorbs the heat, converting it into steam.
3. Steam Generation
The water in the boiler tubes heats up to its boiling point and turns into steam. The pressure inside the boiler causes the steam to become superheated, reaching temperatures as high as 540°C (1004°F) or more, depending on the design.
4. Steam Flow
The superheated steam is then directed to the steam turbine, where it expands and cools as it spins the turbine blades. This mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by a generator connected to the turbine.
5. Condensation and Recirculation
After leaving the turbine, the steam is cooled and condensed back into water in a condenser. This water is then pumped back into the boiler to be reheated, completing the cycle.
6. Control Systems
Modern boilers are equipped with sophisticated control systems that regulate temperature, pressure, and fuel flow to maintain efficient and safe operation.
In summary, a power plant boiler converts the chemical energy of fuel into thermal energy, which is then used to generate steam. This steam drives turbines that produce electricity, forming the core of the power generation process.
Get your best price
Quickly compare 3 FREE quotes
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
25 years+ of boiler R&D
More than 20 innovative technologies

