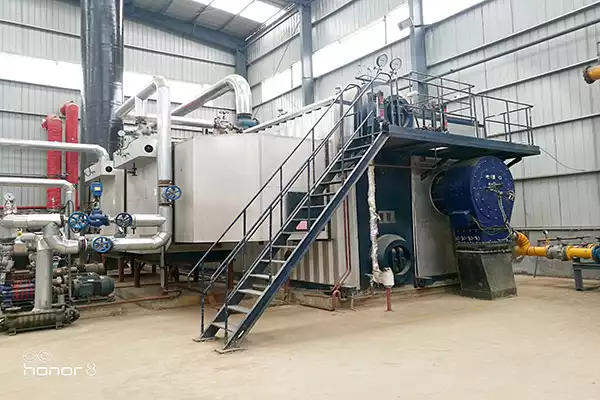
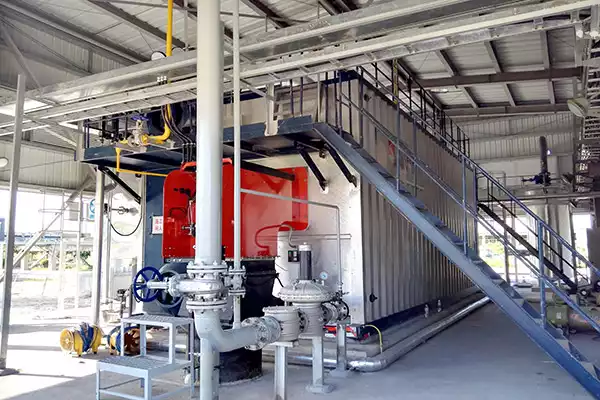
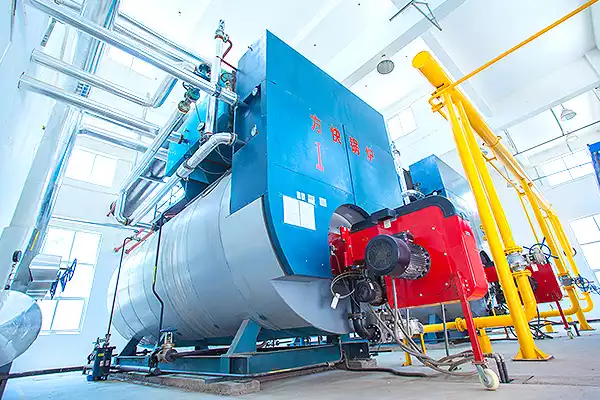
Triple Pass Oil Boilers are widely popular in the world. The reason behind the widespread popularity of triple pass oil boilers is that it is less expensive as compared to other types of boilers and are also more efficient. A triple-pass boiler operates on a three-way system (hence the name) which means that there are three circuits running simultaneously in it. It also reduces carbon emissions by recycling heat from every circuit back into the same circulation loop thus making it cost-effective for both users and manufacturers alike.
Introduction.
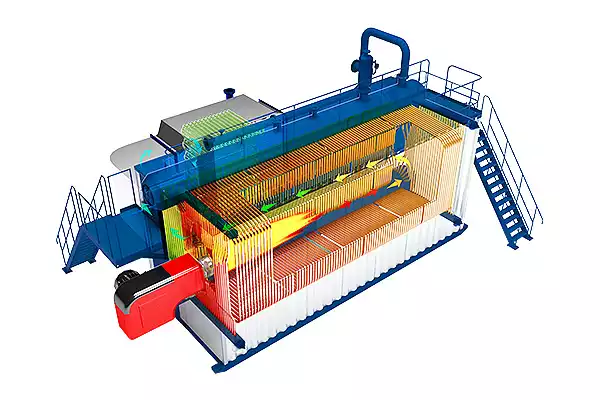
A triple pass oil boiler is a type of oil-fired boiler that uses oil as a fuel source to generate heat. The term “triple pass” refers to the design of the boiler’s combustion chamber and heat exchanger.
In a triple pass oil boiler, the combustion gases produced during the burning of oil pass through the boiler in three separate passes. Each pass allows the gases to transfer heat energy to the water or steam within the system more efficiently.
Working principle.
- First pass: The combustion gases are directed into the first pass, where they travel across the surface of the heat exchanger. During this pass, a significant amount of heat is transferred from the hot gases to the water or steam. As the gases move across the heat exchanger, they begin to cool down.
- Second pass: The partially cooled combustion gases then move into the second pass, where they change direction and flow in the opposite direction of the first pass. This allows for further heat exchange as the gases continue to give off heat to the water or steam.
- Third pass: Finally, the combustion gases enter the third pass, where they travel across the remaining surface area of the heat exchanger. By this stage, the gases have cooled significantly, and any remaining heat is transferred to the water or steam before being exhausted through the flue.
The triple pass design increases the overall heat transfer efficiency of the boiler. By providing multiple opportunities for heat exchange, the system can extract more heat from the combustion gases, maximizing energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption.
Life expectancy.
On average, a well-maintained triple pass oil boiler can last anywhere from 15 to 30 years or even longer. The lifespan of a triple-pass oil boiler can vary depending on various factors, including the quality of the boiler, its maintenance, usage patterns, and environmental conditions. If you want to extend the life of your boiler as much as possible, be sure to follow these tips:
- Use top-quality fuel oil for your boiler
- Have your filters changed regularly (every 6 months)
- Do not put solvents in the drain pan
- Keep an eye out for signs of rust or corrosion
Pros & Cons.
Pros:
- High Efficiency: Triple pass oil boilers are known for their high efficiency in heat transfer. The three-pass design allows for maximum heat extraction from the combustion gases, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced fuel consumption.
- Consistent Heat Output: Triple pass boilers provide a consistent and even heat output, ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. The multiple passes and extended heat exchange surface area contribute to maintaining a steady supply of heat.
- Fuel Flexibility: Triple pass oil boilers can utilize different types of heating oil, such as No. 2 heating oil or biodiesel blends, providing flexibility in fuel choices. This can be advantageous in regions where oil is readily available and affordable.
- Durability: These boilers are often built with durable materials and robust construction, making them long-lasting and able to withstand demanding operating conditions.
Cons:
- Dependency on Oil: One of the significant disadvantages of triple pass oil boilers is their dependency on oil as a fuel source. This reliance on oil can lead to higher fuel costs compared to other energy sources, and it also makes the system vulnerable to fluctuations in oil prices.
- Environmental Impact: Oil combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. While modern triple pass boilers are designed to minimize emissions, they still produce some CO2. This makes them less environmentally friendly compared to renewable energy heating options, such as solar or geothermal systems.
- Storage Space: Oil boilers require storage tanks to hold the fuel, which takes up additional space in the building. This can be a disadvantage for properties with limited storage space or for those preferring a more compact heating system.
- Maintenance and Servicing: Triple pass oil boilers require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning, inspection, and occasional repairs, which can add to the overall cost and inconvenience.
- Combustion Byproducts: Like any combustion-based heating system, triple pass oil boilers produce combustion byproducts, such as soot, particulate matter, and sulfur emissions. Adequate venting and proper maintenance are necessary to minimize these emissions and ensure safe indoor air quality.
2 pass vs 3 pass vs 4 pass.
The difference between 2-pass, 3-pass, and 4-pass boilers lies in the number of times the combustion gases pass through the boiler’s heat exchanger before being exhausted. Each pass allows for additional heat transfer, improving the overall efficiency of the boiler. Here’s a breakdown of these boiler configurations:
- 2-pass Boiler: A 2-pass boiler has two passes for the combustion gases. The gases flow through the first pass and then reverse direction to flow through the second pass. In each pass, heat is transferred from the gases to the water or steam within the system. While 2-pass boilers offer improved efficiency over single-pass designs, they are generally less efficient than triple or quadruple-pass boilers.
- 3-pass Boiler: A 3-pass boiler, also known as a triple-pass boiler, features three passes for the combustion gases. In the first pass, the gases flow across the heat exchanger surface in one direction, then reverse direction in the second pass, and finally, flow in the opposite direction in the third pass. This triple-pass design provides more opportunities for heat exchange and significantly enhances the boiler’s efficiency compared to 2-pass models.
- 4-pass Boiler: A 4-pass boiler has four passes for the combustion gases. Similar to the 2-pass and 3-pass configurations, the gases change direction between passes. The specific arrangement of the passes may vary depending on the boiler design. The extra pass in a 4-pass boiler offers additional heat transfer, potentially further improving efficiency. However, it’s worth noting that 4-pass boilers are less common than 2-pass and 3-pass boilers.
Prices.
The cost of a triple pass oil boiler typically ranges from $3,500 to $8,500 or more. The cost of it can vary depending on several factors, including the brand, model, heating capacity, efficiency rating, and any additional features or components. Additionally, market conditions, geographical location, and installation costs can also influence the overall price.
| Boiler Size (BTU/Hr) | Efficiency Rating (%) | Cost Range ($) |
|---|---|---|
| 50,000 – 70,000 | 85 – 90 | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| 70,000 – 90,000 | 85 – 90 | $3,500 – $6,000 |
| 90,000 – 110,000 | 85 – 90 | $4,000 – $7,000 |
| 110,000 – 130,000 | 85 – 90 | $4,500 – $8,000 |
| 130,000 – 150,000 | 85 – 90 | $5,000 – $9,000 |
Conclusion.
The triple pass oil boiler has been around for many years and has proven to be very efficient because it uses less energy than other types of boilers available today. The triple pass boiler was originally used for heating homes but now it can be used in different industries like power plants that require large amounts of steam at high temperatures or pressure levels.
Get your best price
Quickly compare 3 FREE quotes
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
25 years+ of boiler R&D
More than 20 innovative technologies